Configuring Ubuntu 24.04 + n8n for use with SSL (SSL certificate from IONOS)
Please use the “Print” function at the bottom of the page to create a PDF.
Valid for VPS and migrated Cloud Servers.
In this article, you will first learn how to install the Ubuntu 24.04 + n8n image on your server. n8n is provided in a Docker container as part of the installation. The n8n image provided by IONOS does not contain an SSL certificate for the IP address supplied, meaning that access is initially only possible via the unencrypted HTTP protocol. In order to access n8n via an encrypted connection, manual configuration is required. How to prepare the configuration and configure n8n is explained later in the article.
Summary of the necessary steps
The necessary steps are listed in brief below:
Install the image on the server
- Prepare configuration
- Establish SSH connection to the server
- Save SSL certificate files on the host
- Create fullchain file
- Configure n8n for SSL connection
- Access the n8n interface
Caution
If you reinstall an image on an existing server, all existing data on the server will be irretrievably deleted and replaced by the data of the newly installed image. This process can no longer be undone. Make sure that you create a backup of the server before installing the image. Otherwise there is a risk of data loss.
Install image on the server
To install the Ubuntu 24.04 + n8n image, complete the following:
- Log in to your IONOS account.
Click on Menu > Servers & Cloud in the title bar.
Optional: If you have multiple server contracts, select the desired contract.
- Click on the desired server in the Infrastructure > Servers area.
- Click on Actions.
- Click on Reinstall Image. The Reinstall Image area is displayed.
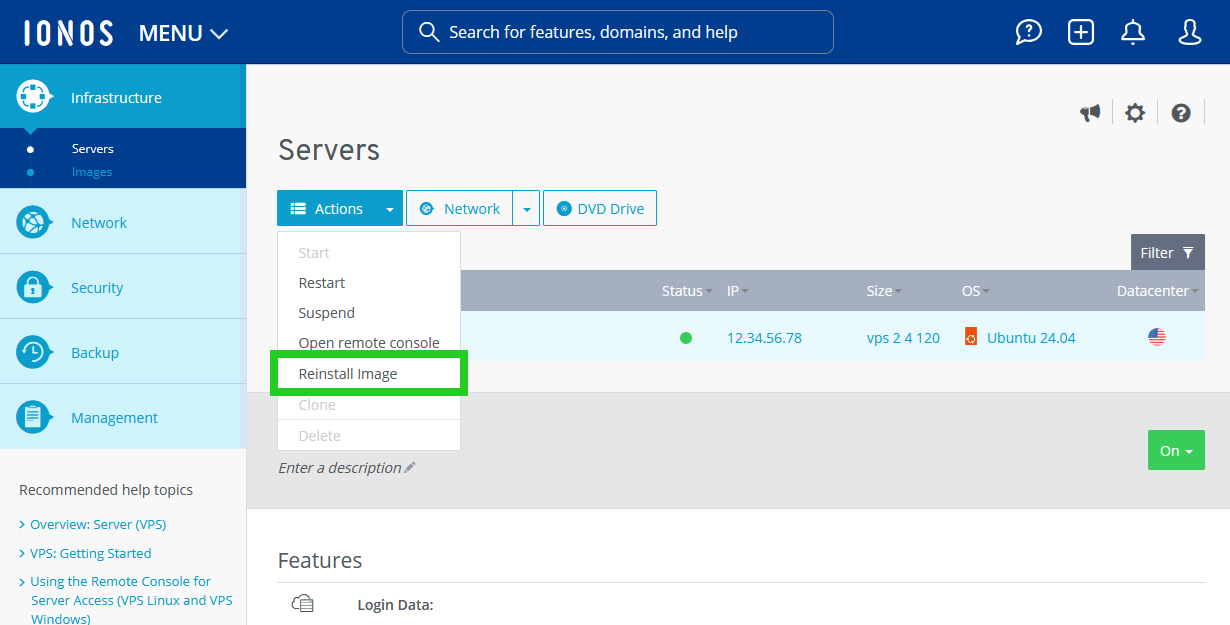
- Click on the arrow pointing downwards in the Ubuntu tile.
- Select the Ubuntu 24.04 + n8n image.
- Click on Reinstall Image. The image is installed. This process may take a few minutes.
- Make a note of the IP address of the server. This will be required later on to connect your domain.
Notes
After installation, port 80, port 443 and port 5678 must be enabled in the firewall. Further information on this can be found in the section Prepare configuration.
After installation, you can access your n8n instance using the IP address of your server and the default port number of n8n: http://IP-ADDRESS_OF_SERVER:5678
Prepare configuration
In order to establish an encrypted connection to n8n, a domain that can be accessed is required. In addition, an SSL certificate is required, which is issued for the domain.
Order a domain
If you have not yet ordered a domain for your server, you can order one at any time. You can find instructions in the following article: Ordering a domain as an IONOS customer
Create a subdomain
Create a subdomain in the following format: n8n.example.com
Replace the placeholder example.com with your chosen domain. How to create a subdomain in your IONOS account is explained in the following article: Creating a subdomain
Ordering an SSL certificate
Set up an SSL certificate for your subdomain. If you have already set up a wildcard SSL certificate for the domain, you can skip this step. Wildcard SSL certificates are valid for both your domain and your subdomain.
If you order an SSL starter certificate, you can use this for your subdomain. The following article explains how to set up an SSL certificate: Setting up a user-managed SSL certificate (SSL Starter / SSL Starter Wildcard)
Download SSL certificate files for manual installation
Instructions on how to download the SSL certificate files for manual installation can be found in the following article: Downloading SSL certificate files for manual installation
Connecting the domain to the static IP address of the server
You can find instructions on how to connect your domain to the static IP address of your server in the following article: Changing the IPv4/IPv6 address of a domain (A/AAAA record)
Configuring the firewall
Make sure that the following ports are enabled in the firewall policy:
Port 80
Port 443
Port 5678
You can find instructions in the following article: Editing the firewall policy (VPS and migrated Cloud Servers)
Establish SSH connection to the server
In the next step, establish an SSH connection to your server. Log in as root for this. You can find corresponding instructions in the following articles:
Establishing an SSH connection to your Linux server on a Microsoft Windows computer
Establishing an SSH connection to your Linux server on a Linux computer
Store SSL certificate files in the host
To save the SSL certificate files on the host, complete the following:
Certificate files are already on the server
Create a folder in the /opt/ directory:
root@ubuntu:~# mkdir -p /opt/certs
Copy the files into the folder. If the certificate files are already on the server, adapt and use the following command:
root@ubuntu:~# cp /path/to/SSL_CERTIFICATE_FOR_DOMAIN.cer /opt/certs/
root@ubuntu:~# cp /path/to/INTERMEDIATE_CERTIFICATE_1.cer /opt/certs/
root@ubuntu:~# cp /path/to/INTERMEDIATE_CERTIFICATE_2.cer /opt/certs/
root@ubuntu:~# cp /path/to/PRIVATE_KEY_FOR_DOMAIN.key /opt/certs/
Certificate files are already on a computer with the Microsoft Windows operating system
If the certificate files are located on a computer with the Microsoft Windows operating system, complete the following:
- Enter the command cmd in the search bar located in the taskbar.
- Double-click on Command Prompt.
Use the scp command to copy the files from Windows to the Linux system. In the following example, we assume that the certificate files are located in the C:\SSL certificate folder. Replace before entering:
username: with your actual user name on the server.
remote-server-ip with the IP address or the host name of your server.
SSL_CERTIFICATE_FOR_DOMAIN.cer and PRIVATE_KEY_FOR_DOMAIN.key with the actual file names.
INTERMEDIATE_CERTIFICATE_1.cer and INTERMEDIATE_CERTIFICATE_2.cer with the actual file names.scp C:\SSL-Certificate\SSL_CERTIFICATE_FOR_DOMAIN.cer username@remote-server-ip:/opt/certs/
scp C:\SSL-Certificate\INTERMEDIATE_CERTIFICATE_1.cer username@remote-server-ip:/opt/certs/
scp C:\SSL certificate\INTERMEDIATE_CERTIFICATE_2.cer username@remote-server-ip:/opt/certs/
scp C:\SSL-Certificate\PRIVATE_KEY_FOR_DOMAIN.key username@remote-server-ip:/opt/certs/
Alternatively, you can transfer the files easily and conveniently using the WinSCP program. WinSCP is a graphical open source SFTP and FTP client for Windows. You can download the program on the following page of the provider: WinSCP Download
Assign read rights
Change to the directory in which the SSL certificates are located. Example:
root@ubuntu:~# cd /opt/certs
To enable the files to be read, enter the following commands on the VPS:
sudo chmod 755 /path/to/certs
sudo chmod 644 /path/to/certs/*
Example
sudo chmod 755 /opt/certs
sudo chmod 644 /opt/certs/*
Create fullchain file
To integrate the intermediate certificates, you must create a single certificate file that contains the entire "chain of trust". To do this, complete the following:
Change to the /opt/certs directory:
root@ubuntu:~# cd /opt/certs
Create a "fullchain" file with the following command. The cat command appends the files in the correct order. Replace the placeholder SSL_CERTIFICATE_FOR_DOMAIN.cer with the SSL certificate for your domain and the placeholders for the intermediate certificates. Make sure that the file names are correct.
root@ubuntu:/opt/certs# cat SSL_CERTIFICATE_FOR_DOMAIN.cer intermediate1.cer intermediate2.cer > n8n.fullchain.cer
The "fullchain" file is created.
configure n8n for SSL connection
Caution
These steps will deactivate the installed, unsecured instance and install a new n8n instance secured with an SSL certificate from IONOS. If you carry out these steps after you have been working with the unsecured instance for some time, we recommend that you first export any workflows and other content you have created so that you can import them into the new instance. You can find out how this works here in the n8n documentation: Exporting and importing workflows | n8n Docs
To create a new directory named n8n-compose on your server, enter the following command:
root@ubuntu:~# mkdir n8n-compose
To continue working in the newly created directory, change to the new directory:
root@ubuntu:~# cd n8n-compose
In this directory, use the vi editor to create a file with the file extension .env. This file is used to define environment variables that are used in the Docker Compose file.
root@ubuntu:~/n8n-compose# vi .env
Notes
The vi editor has an insert mode and a command mode. You can call up insert mode with the [i] key. In this mode, the characters entered are immediately inserted into the text. To exit insert mode and call up command mode, press [ESC]. If you use command mode, your keyboard input is interpreted as a command.
Add the information below to the .env file and replace the placeholder example.com and the placeholder for the time zone. These variables will be referenced in the compose.yaml file in a later step and are used to define domain settings and the desired time zone standard.
# DOMAIN_NAME and SUBDOMAIN together determine where n8n will be reachable from
# The top level domain to serve from
DOMAIN_NAME=example.com
# The subdomain to serve from
SUBDOMAIN=n8n
# The above example serves n8n at: https://n8n.example.com
# Optional timezone to set which gets used by Cron and other scheduling nodes
GENERIC_TIMEZONE=America/New_York- Press the [ESC] key.
To exit vi and save the file, enter the following command and then press the Enter key:
:wq
Use the following command to create the file traefik.yaml:
root@ubuntu:~/n8n-compose# vi traefik.yaml
Insert the following information, paying attention to the indentations:
# Static Traefik configuration (traefik.yaml)
api:
insecure: true # Allows the Traefik dashboard (optional)
providers:
docker:
exposedByDefault: false # Only containers with 'traefik.enable=true' are taken into account
file:
directory: /etc/traefik/dynamic # Path *in container*
watch: true # Watch for changes
entryPoints:
web:
address: ":80"
# Automatic forwarding from HTTP to HTTPS
http:
middlewares:
- redirect-to-https@file
websecure:
address: ":443"
http:
tls: {} # Activate TLS globally for this entrypoint- Press the [ESC] key.
To exit vi and save the file, enter the following command and then press the Enter key:
:wq
Create a new directory with the name dynamic:
root@ubuntu:~/n8n-compose# mkdir dynamic
Create a dynamic certificate file:
root@ubuntu:~/n8n-compose# vi dynamic/certificates.yaml
Insert the following information and replace the placeholder PRIVATE_KEY_FOR_DOMAIN.key. Pay attention to the indentations:
# Dynamic configuration: Certificates
tls:
certificates:
# Path *inside the container* to the chain
- certFile: /opt/certs/n8n.fullchain.cer
keyFile: /opt/certs/PRIVATE_KEY_FOR_DOMAIN.key
# Dynamic configuration: Global HTTP-to-HTTPS forwarding
http:
middlewares:
redirect-to-https:
redirectScheme:
scheme: https
permanent: true- Check the paths in the lines certFile and keyFile and adjust them if necessary.
- Press the [ESC] key.
To exit vi and save the file, enter the following command and then press the Enter key:
:wq
Create a directory with the name local-files. This is used as a bind mount to enable access to files from the container. To do this, enter the following command:
root@ubuntu:~/n8n-compose# mkdir local-files
To create the required Docker Compose file, enter the following command:
root@ubuntu:~/n8n-compose# vi compose.yaml
Add the information below and make sure that the entries in the section # Definition of the security header middleware (name: n8n-secure-headers) are on one line.
services:
traefik:
image: "traefik:v2.11" # Fixed version for stability
restart: always
command:
- "--configFile=/etc/traefik/traefik.yaml"
ports:
- "80:80"
- "443:443"
- "127.0.0.1:8080:8080"
volumes:
- traefik_data:/data # Internal memory for Traefik (e.g. ACME info, if used)
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro
# Mount the certificates (as before)
- /opt/certs:/opt/certs:ro
# Mount the new static config file
- ./traefik.yaml:/etc/traefik/traefik.yaml:ro
# Mount the new dynamic config folder
- ./dynamic:/etc/traefik/dynamic:ro
n8n:
image: docker.n8n.io/n8nio/n8n
restart: always
ports:
- "127.0.0.1:5678:5678"
labels:
- traefik.enable=true
- traefik.http.routers.n8n.rule=Host(`${SUBDOMAIN}.${DOMAIN_NAME}`)
# The router only listens for 'websecure' (HTTPS)
- traefik.http.routers.n8n.entrypoints=websecure
# Tells the router to use TLS
- traefik.http.routers.n8n.tls=true
# Definition of the security header middleware (name: n8n-secure-headers)
- traefik.http.middlewares.n8n-secure-headers.headers.STSSeconds=315360000
- traefik.http.middlewares.n8n-secure-headers.headers.browserXSSFilter=true
- traefik.http.middlewares.n8n-secure-headers.headers.contentTypeNosniff=true
- traefik.http.middlewares.n8n-secure-headers.headers.forceSTSHeader=true
- traefik.http.middlewares.n8n-secure-headers.headers.SSLHost=${DOMAIN_NAME}
- traefik.http.middlewares.n8n-secure-headers.headers.STSIncludeSubdomains=true
- traefik.http.middlewares.n8n-secure-headers.headers.STSPreload=true
# Assignment of the middleware to the router
- traefik.http.routers.n8n.middlewares=n8n-secure-headers@docker
environment:
# These environment variables use the .env file
- N8N_ENFORCE_SETTINGS_FILE_PERMISSIONS=true
- N8N_HOST=${SUBDOMAIN}.${DOMAIN_NAME}
- N8N_PORT=5678
- N8N_PROTOCOL=https
- N8N_RUNNERS_ENABLED=true
- NODE_ENV=production
- WEBHOOK_URL=https://${SUBDOMAIN}.${DOMAIN_NAME}/
- GENERIC_TIMEZONE=${GENERIC_TIMEZONE}
- TZ=${GENERIC_TIMEZONE}
volumes:
- n8n_data:/home/node/.n8n
- ./local-files:/files
volumes:
n8n_data:
traefik_data:
- Press the [ESC] key.
To exit vi and save the file, enter the following command and then press the Enter key:
:wq
To find out which process is using port 5678, enter the following command:
root@ubuntu:~/n8n-compose# sudo lsof -i :5678
To terminate a process, customise the following command and enter it:
root@ubuntu:~/n8n-compose# sudo kill INSERT_PID_HERE
After customisation, enter the following command to stop the old containers:
root@ubuntu:~/n8n-compose# docker compose down
To start the containers defined in compose.yaml as daemons in the background, enter the command below. This command starts and configures the Traefik and n8n instances.
root@ubuntu:~/n8n-compose# docker compose up -d
To check whether the containers are running, enter the following command:
root@ubuntu:~/n8n-compose# docker ps
Make sure that the following 2 containers are running and their status is "UP". To do this, enter the following commands.
root@ubuntu:~/n8n-compose# n8n-compose-traefik-1
root@ubuntu:~/n8n-compose# n8n-compose-n8n-1
Troubleshooting issues
If one of the containers does not have the status "Up" (e.g. "Restarting" or "Exited"), this indicates an error. In this case, check the Traefik log entries. To do this, enter the following command:
root@ubuntu:~/n8n-compose# docker logs n8n-compose-traefik-1
Then search for error messages, such as
certificate not found
unable to read
permission denied (this would indicate a chmod problem)
router not found for domain- Check the firewall settings in Cloud Panel and make sure that incoming traffic is authorised for port 80 (TCP) and port 443 (TCP).
- Check the accessibility of the subdomain.
- Check the indentation of the .yaml files.
Accessing the n8n interface
Once the Docker services (containers) have been successfully started, access to n8n is managed by the Traefik proxy. Traefik ensures SSL encryption and forwards requests to your n8n instance. Access is now exclusively via the domain that you have previously configured in the .env file.
Note
Direct access via http://SERVER-IP:5678 is no longer possible. The configuration in compose.yaml (under ports: - "127.0.0.1:5678:5678") ensures that n8n is only accessible "internally" (for Traefik), but not publicly via the server IP.
- Open your browser.
- Enter the complete, secure URL, which is made up of the variables SUBDOMAIN and DOMAIN_NAME of your .env file. Example:
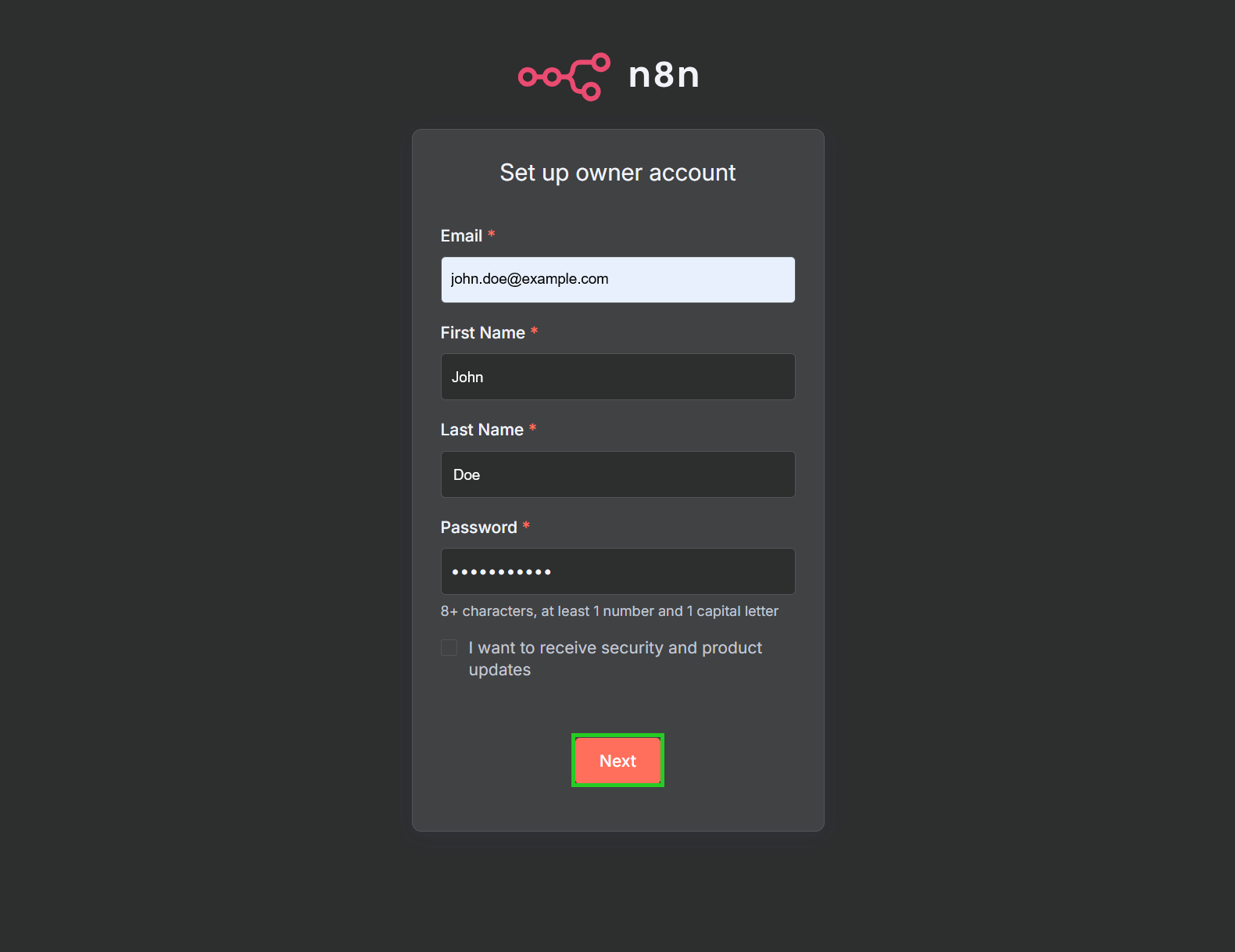
https://n8n.example.com - The Set up owner account window is displayed the first time you open it. Enter the desired email address in the Email field.
- Enter your first and last name in the First Name and Last Name fields.
- Enter a password in the Password field.
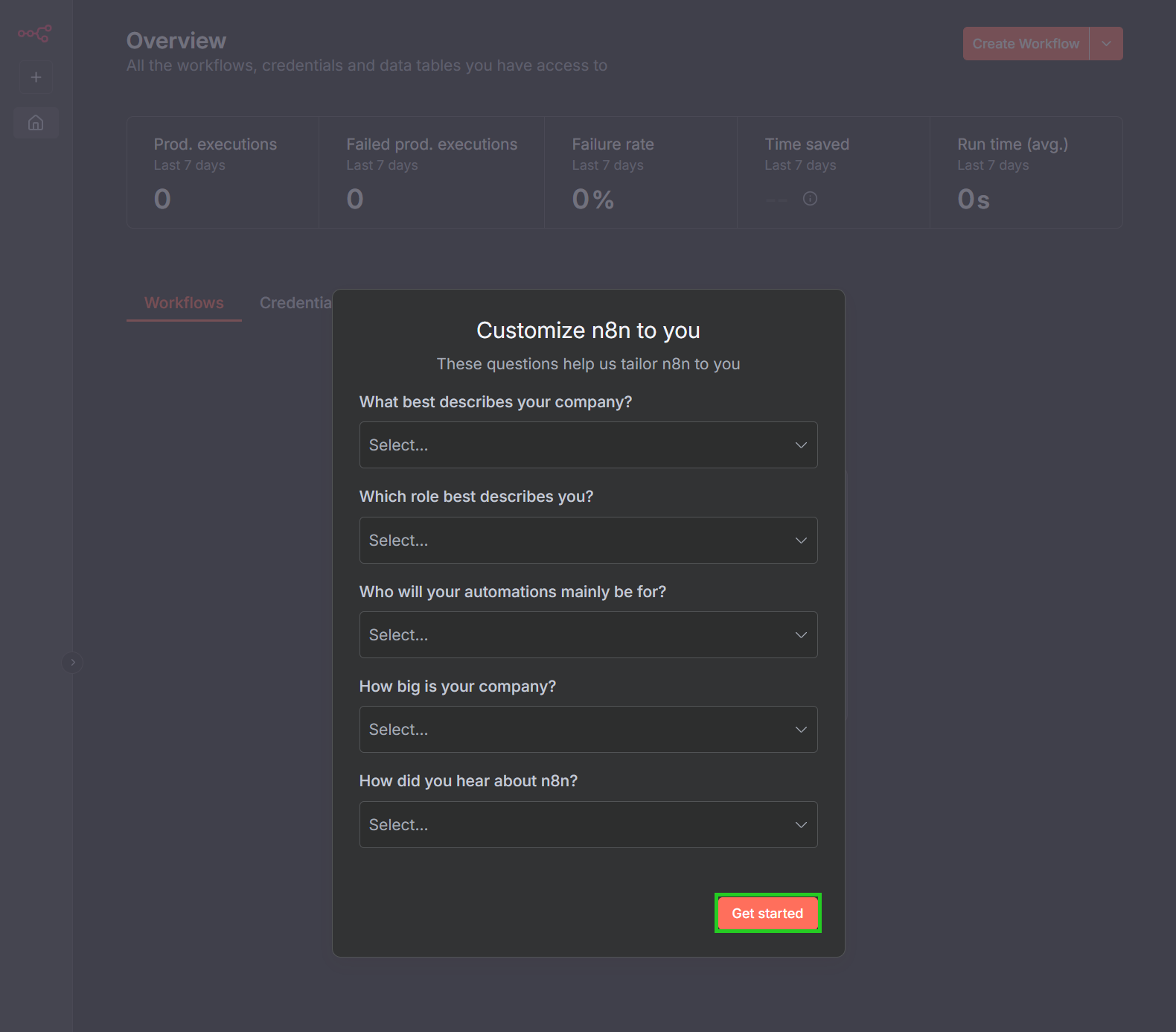
- Click on Next. The Customize n8n to you window opens.
- Answer the questions in the Customize n8n to you window and click on Get started. You can now use n8n.