How to enable and disable hibernation in Windows 10
Hibernation conserves energy and battery life, and lets you continue your work where you left off even after a long break away from your screen. It can be activated and deactivated in Windows 10 via the power settings. Read on to find out how to adjust hibernation settings in Windows 10.
- Up to 50 GB Exchange email account
- Outlook Web App and collaboration tools
- Expert support & setup service
Why is Windows 10 hibernate useful?
To understand the benefits of Windows 10 hibernation, it’s important to understand what it does. When your device goes into hibernation mode, the system saves all opened files, applications, and documents to disk (not to RAM memory). Consequently, the system turns off the screen and background programs, but also shuts down the entire power supply, conserving battery power and saving electricity costs. When you wake the device from hibernation, any previously opened applications are reloaded and you can continue where you left off.
Energy saving options in Windows 10
Hibernation is one of three energy-saving settings in Windows 10. It is the only option that shuts off power completely:
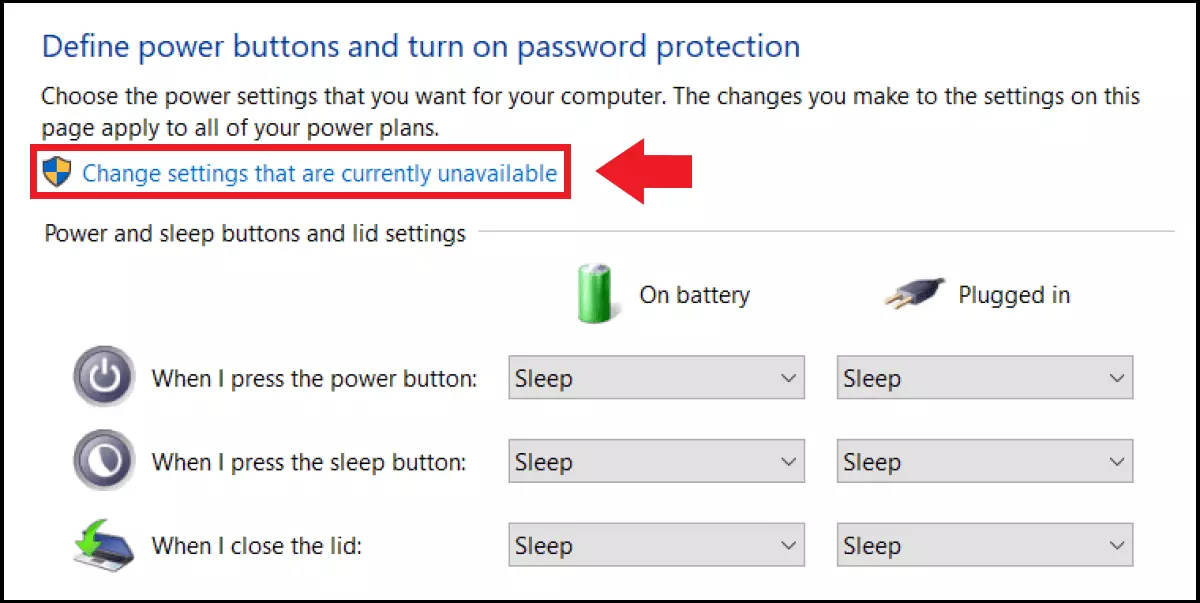
- Hibernation: Stops all opened documents, files and applications on the hard drive and interrupts the power supply. The device is no longer powered. Once you resume, the system continues where you left it. Hibernation is disabled by default in Windows 10. To use it, you need to switch it on first.
- Standby mode: Standby and hibernation differ in that only the screen and unnecessary background programs are stopped in standby. Opened files, documents and applications are saved in the RAM. The device is still powered and can be woken up faster compared to hibernation.
- Hybrid hibernation: In hybrid hibernation, your device backs up existing documents, files, and applications to memory and hard drives. Power consumption is reduced to a minimum. The advantage is that work is loaded via the hard disk. To protect your data from being lost, it is recommended that you regularly perform a Windows 10 backup.
Enable hibernate in Windows 10: tutorial
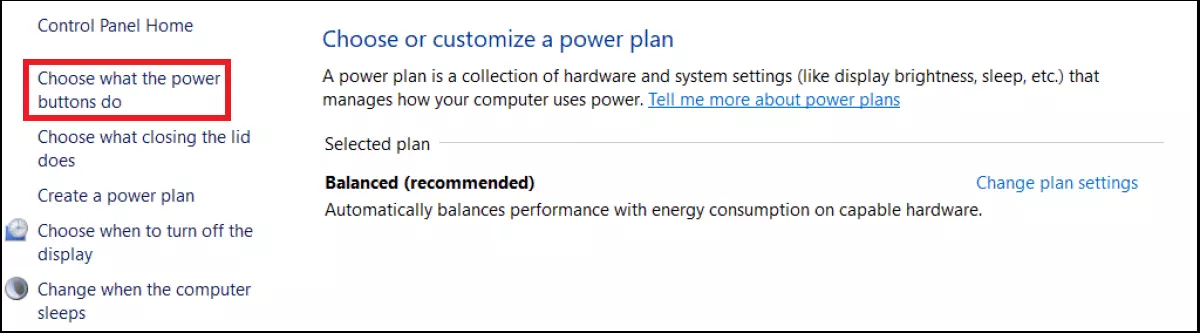
To enable hibernate in Windows 10, follow the steps below.
If you want to enable hibernate in Windows 11, follow ‘System’ > ‘Power & Battery’ and access the display settings.
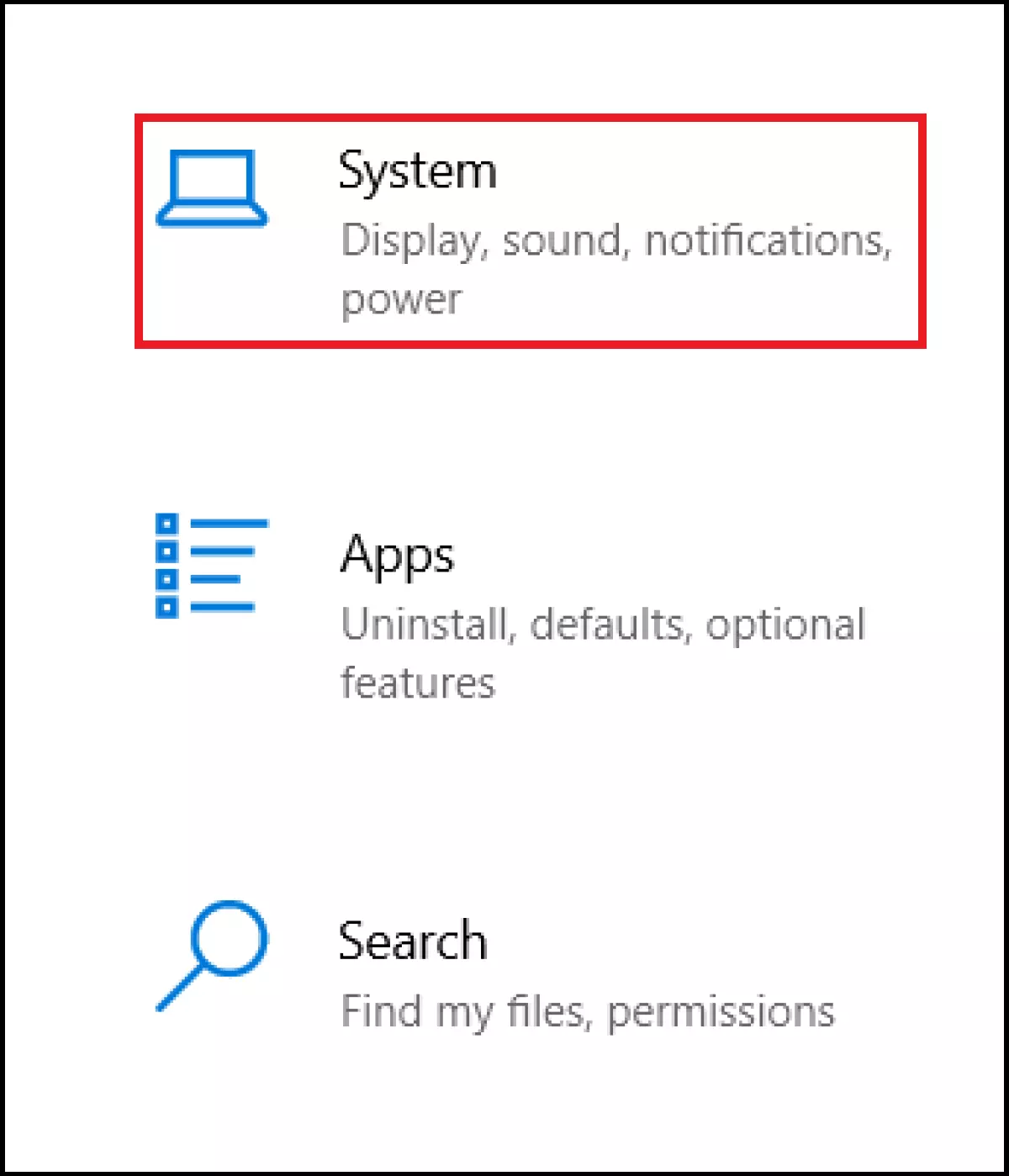
Step 1: Launch the Windows settings using the Windows shortcut [Windows] + [i] and access ‘System’.
Disable Windows 10 hibernate
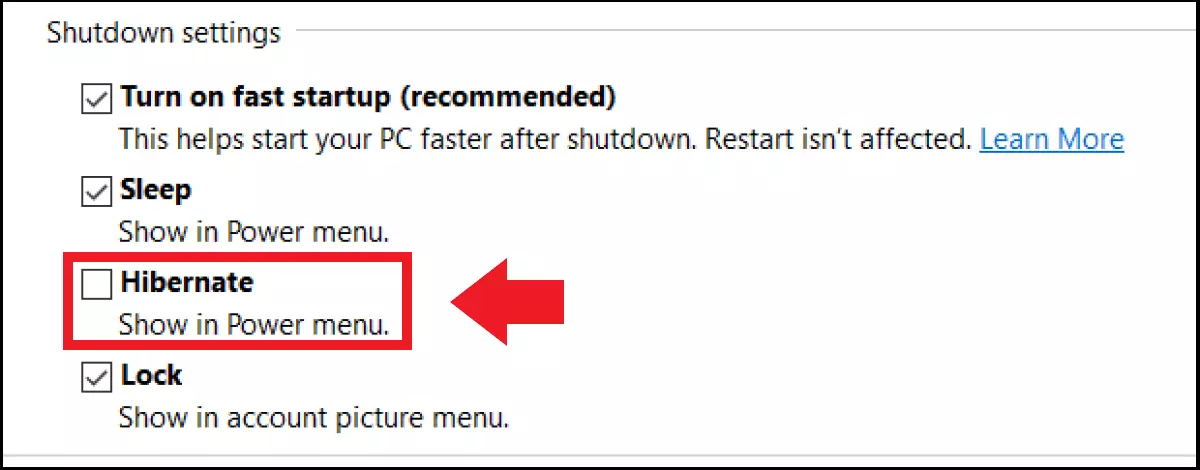
Sometimes you may wish to disable Windows 10 hibernation, perhaps to speed up Windows 10 or prevent your laptop from ‘falling asleep’ all the time. To do so, simple remove the tick next to ‘Hibernate’ in the power options menu. If you wish to disable Windows 10 sleep mode rather than Hibernate, remove the corresponding tick next to ‘Sleep’. Since both functions are useful to save energy, you should leave the standby/power-saving mode enabled.