How to create and apply a Kubernetes load balancer
A Kubernetes load balancer automatically distributes network traffic across multiple pods to ensure even load distribution and high availability. It is typically implemented through a ‘LoadBalancer’ type service that forwards external requests to internal services. This way, applications can be made reliably and scalably accessible.
The ideal platform for demanding, highly scalable container applications. Managed Kubernetes works with many cloud-native solutions and includes 24/7 expert support.
What is a load balancer in Kubernetes?
Load balancers distribute the workload across servers or virtual machines as efficiently as possible, helping to boost the overall performance of the system. Positioned in front of the servers, a load balancer prevents individual machines from becoming overloaded and ensures optimal use of available resources. Even if a server fails, load balancing keeps the system running smoothly by intelligently redirecting requests.
Kubernetes load balancers operate a bit differently—but with the same underlying concept. In Kubernetes, however, distinction must be made between two different types of load balancers:
- Internal Kubernetes load balancers
- External Kubernetes load balancers
Internal Kubernetes load balancers
Internal Kubernetes load balancers take a different approach than classic load balancers and are mentioned here for completeness. They ensure that only applications running within the same virtual network as their Kubernetes cluster can access this network.
External Kubernetes load balancers
External load balancers assign a specific IP address or a DNS name to a service node of a Kubernetes cluster, allowing it to receive external HTTP requests. The ‘LoadBalancer’ is a special Kubernetes service type designed to forward external traffic to individual Kubernetes pods within the cluster, ensuring an optimal distribution of incoming requests.
There are several options or algorithms to configure load balancing in Kubernetes. The one you choose depends entirely on your individual needs. The different algorithms primarily determine the principle by which the load balancer processes incoming traffic.
How does a load balancer work?
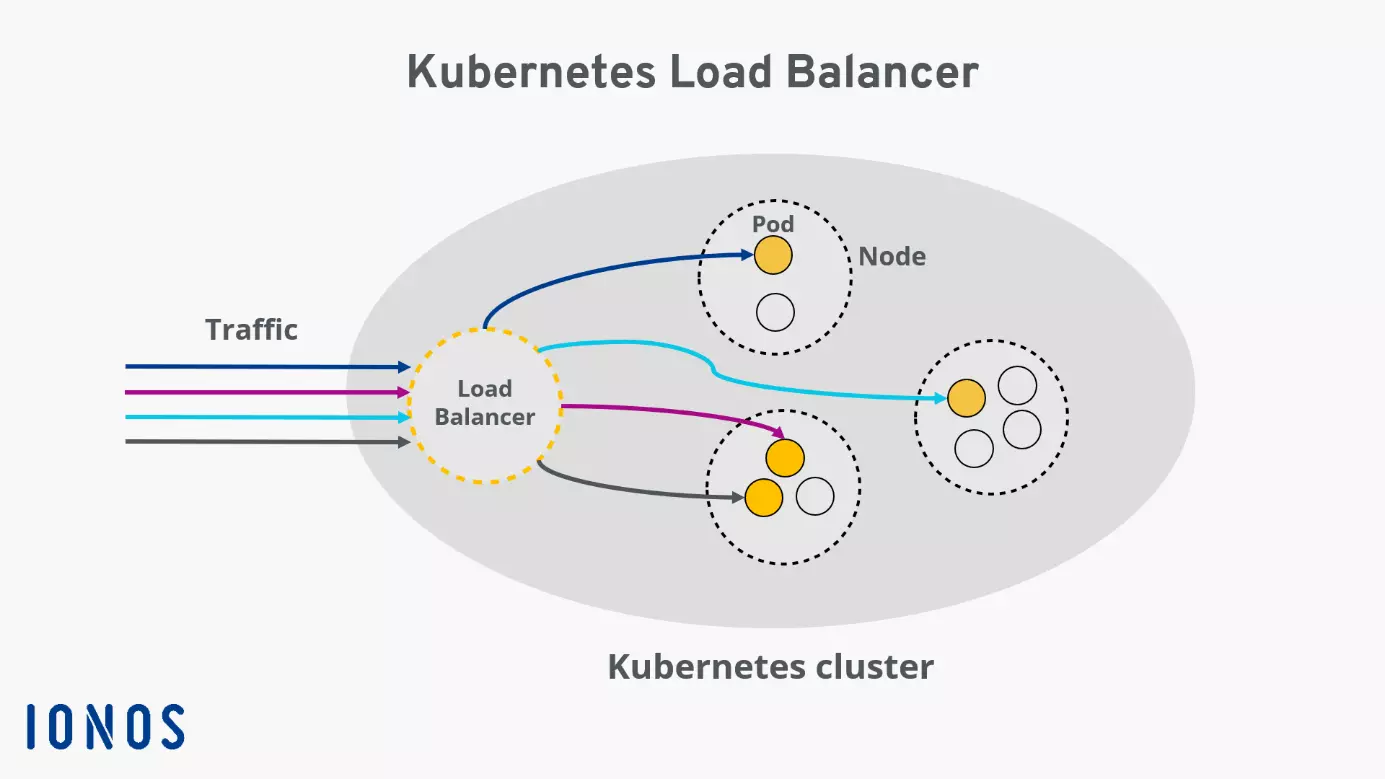
In Kubernetes, a load balancer takes on the central task of efficiently distributing network traffic across multiple instances of a service, namely the pods. The goal is to ensure balanced utilisation, increase availability, and compensate for the failure of individual components.
Technically, the load balancer receives incoming requests and checks which pods are currently available and efficient. Kubernetes uses continuous internal monitoring for this purpose: Pods that are faulty or overloaded are automatically excluded from routing. The load balancer then dynamically decides which pod to forward each request to.
This distribution is based on various criteria. Users are unaware of this process. The application remains accessible and high performing, even when individual pods start, are redeployed, or fail in the background.
- Total control over your data
- Benefit from the highest security standards
- No vendor lock-in for maximum flexibility
What is a Kubernetes load balancer for?
A Kubernetes load balancer defines a service running within the cluster that is accessible over the public internet. To understand this, it’s helpful to look at the Kubernetes architecture. A cluster includes multiple nodes, each containing several pods. Each pod in the cluster is assigned an internal IP, which cannot be accessed from outside the cluster.
Making software available under a fixed IP
To make the software running in pods usable under a dedicated IP address, a Kubernetes service is typically required. Besides ‘LoadBalancer’, there are other service types suitable for various scenarios. All service types share the characteristic of grouping a set of pods into a logical unit and describing how they can be accessed.
Optimal distribution of external traffic
A Kubernetes load balancer is designed to ensure optimal distribution of external traffic to the pods in your Kubernetes cluster. This makes these services suitable for virtually any use case. Since Kubernetes load balancers can direct traffic specifically to individual pods, high availability of your cluster is guaranteed: If a pod becomes non-functional or exhibits errors, the load balancer ensures that tasks are distributed to the other pods.
Optimising scalability
Scalability is also positively impacted by the use of load balancing. Kubernetes can automatically create or delete pods as needed. Thus, if it is determined that incoming traffic requires more or fewer resources than currently available, Kubernetes can automatically respond to this situation.
How to create a load balancer for Kubernetes
To create a Kubernetes load balancer, your cluster must run in a cloud or an environment that supports the configuration of external load balancers.
At IONOS, a static IP is assigned to a node in the cluster when a Kubernetes load balancer is created. This IP allows the service to be accessed from outside the cluster. The Kube-Proxy running on the node intelligently distributes incoming traffic to the individual pods.
First, create a service and then set the service type to LoadBalancer by adding the following line to the service manifest:
type: LoadBalancerFor example, the configuration of a Kubernetes load balancer might look like this: The service groups pods under the ‘web-app’ selector. Incoming traffic on port 8080 under the load balancer IP is distributed to the individual pods, addressing the service running on each pod at port 80:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: web-app-service
spec:
selector:
app: web-app
type: LoadBalancer
loadBalancerIP: 203.0.113.0
ports:
- name: http
port: 8080
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCPAnother way to create a Kubernetes load balancer is through the kubectl command line.
With the command
kubectl expose deployment test --target-port=9376 \
--name=test-service --type=LoadBalancercreate and deploy a new service named ‘test-service’ that functions as a load balancer.
If you want to find out the IP address of your newly created service, the following command will help:
kubectl describe services test-service
