How to distribute server workloads with a load balancer
Using Load Balancing allows server access to be evenly distributed across various hardware resources through a technical instance called a Load Balancer. This ensures stable access speeds, which is crucial for generating leads and customers.
- 1 Gbit/s bandwidth & unlimited traffic
- Minimum 99.99% uptime & ISO-certified data centres
- 24/7 premium support with a personal consultant
What is load balancing?
Load balancing is especially popular in server technology and describes a method where requests are distributed among different servers in the background without users noticing. The load balancer used for this can be implemented as hardware or software. It assigns several servers to a domain without causing address conflicts and is accessed under the public domain.
Typically, each domain is assigned to only one web server. If it fails due to overload, the user receives an error message in the form of an HTTP status code: The website cannot then be displayed.
The subordinate web servers are named with the domain additions www1, www2, www3, etc. This allows load balancing to make a website available under the same URL, even though multiple servers are behind it. This prevents server overload as external requests are distributed across various physical machines within the cluster. Users generally do not notice this because the distribution of requests happens based on complex algorithms in the background.
Load balancing can also play a role beyond web servers, such as with computers that operate with multiple processors. In such cases, the load balancer ensures that demands are evenly distributed across the different processors to generate more computing power. Load balancers are also in demand when using container software like Kubernetes. Here, they ensure that workloads are efficiently distributed across various pods.
How does load balancing work?
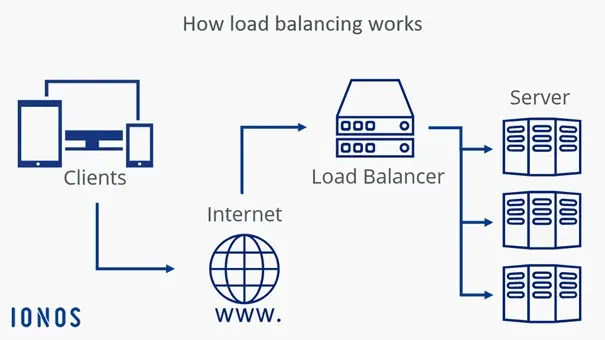
Requests to a web server, e.g. in the form of page views, initially run on the load balancer. This then takes over the load distribution by forwarding the access attempts to different servers. The load balancer itself can be implemented as hardware or software, but the principle remains the same: a request reaches the load balancer and, depending on the method used, the device or software forwards the data to the relevant server.
The technical basis is the DNS procedure: Users access a website only through a URL. This is converted into an IP address using the DNS, which then points to the load balancer. Ideally, this process goes unnoticed by users.
What are the benefits of balanced load balancing?
The three main advantages of a well-deployed load balancer are as follows:
- Optimised access times: Distributing traffic across multiple servers can result in shorter access times, even when there are many requests at the same time.
- Higher fault tolerance: A load balancer increases fault tolerance as the traffic from a slow server is automatically redirected to other servers in the cluster. If a server is unavailable, the hosted website remains accessible.
- Simplified system maintenance: Load balancing greatly supports maintaining a server system. Configurations and updates can be performed while the servers are running without noticeable performance loss. The load balancer detects maintenance states and redirects requests accordingly.
What are the different types of load balancing?
How incoming requests are distributed depends on the choice of algorithm. Popular algorithms for load balancing are: Round Robin, Weighted Round Robin, Least Connections, and Weighted Least Connections.
Round Robin
Round Robin describes a procedure whereby incoming server requests are processed in a queue by the load balancer and distributed throughout a series of servers. Each new request is assigned to the next server in the sequence. As a result, access requests can be evenly spread across the load balancing cluster. No matter how urgent the request or severity of the server load, Round Robin treats all processes the same. Load balancers that operate on the round-robin principle is especially suitable for environments where all instances have about the same resources available.
Weighted Round Robin
The weaknesses of the classic round-robin algorithm in heterogeneous server clusters can be balanced with a weighted round-robin distribution. Incoming requests are distributed considering the static weighting of each server. This weighting is defined in advance by the administrator.
The most powerful server, for example, can be assigned the value ‘100’, while less efficient servers are given the value ‘50’. In such a setup, the server weighted ‘100’ would receive two requests per round from the load balancer, whereas the server weighted ‘50’ would receive only one request. Weighted Round Robin should primarily be used in load balancing when the servers in the cluster have different resources available.
Least Connections
Both round-robin algorithms do not take into account, during the serial distribution of server requests by the load balancer, how many connections the subordinate servers must maintain over a certain period. This can result in several connections piling up on one server in the cluster. This leads to the server becoming overloaded, even if it handles fewer connections than others. The least-connections algorithm protects against this. It distributes requests based on the existing connections of each server—the one with the fewest active connections gets the next request from the load balancer. This load-balancing method is recommended for homogeneous server clusters where all computers have comparable resources available.
Weighted Least Connections
If a server cluster has different capacities, instead of the least-connections algorithm, load balancing based on the weighted distribution of existing connections should be used. This considers both the number of active connections a server has and the weighting defined by the administrator. This ensures a balanced load distribution within the server cluster. New requests are automatically assigned by the load balancer to those servers whose ratio of active connections to their respective server weighting suggests the least current load.
What problems can arise when using load balancing?
Especially in the E-Commerce sector, load balancing often faces challenges. Here’s an example: Website visitors add items to their shopping basket that they wish to purchase. These items remain saved for the duration of a session, regardless of which page the users navigate to within the online marketplace. A typical load balancer would distribute requests across different servers. This means the contents of the basket would be lost.
To solve this problem, two approaches are conceivable. First, the load balancer can respond to the IP address of the users. Then, for example, requests from the same IP address are always directed to the same server. Another method would be to read a session ID from the request itself to determine which server the request must be sent to.
Why are load balancers so important?
If you earn your money over the internet, your business can’t afford a server outage. And if you use only one server and it crashes due to overload, your website is no longer accessible to potential customers. This leads to several problems: For one, you can’t generate revenue during the overload. Services can’t be booked and purchases can’t be made. Additionally, trust from (potential) customers decreases. It’s doubly bad for users who experience a server overload during the order process. There is often great uncertainty, and those affected don’t know if the order actually arrived and was recorded in the system.
Even if you don’t offer services directly over the internet, your website should be accessible at all times. A website is one of the primary channels for accessing information. If potential customers look for details about your company online and can’t reach your site, they are more likely to consider your competition. You can minimise such risks with a load balancer.
How to implement load balancing in your business
Load balancing can be implemented using both hardware and software solutions on a virtual server. Professional complete packages are offered by numerous providers either as Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) or as a network component for your own IT infrastructure.
Since the acquisition of proprietary load balancers usually involves high costs, smaller companies often turn to open-source solutions like NGINX. It offers a cost-effective way to ensure high availability for your company website or other web projects through efficient load distribution within the server network. In the web hosting sector, load balancing is also often offered as an add-on feature for cloud servers.

