How to set up your Drupal website step by step
In this Drupal tutorial, you’ll learn what sets the CMS apart, the requirements for using the open-source software, and how to create a simple Drupal website.
- Loading 3x faster for happier customers
- Rock-solid 99.99% uptime and advanced protection
- Only at IONOS: up to 500 GB included
What is Drupal?
Drupal is a content management system freely licensed under the GNU General Public License, with its first official version released in 2001. Like many comparable systems, it is written in the scripting language PHP and has a modular structure: There are seven core modules and thousands of additional modules. The core modules provide the basic functions and thus the foundation for any website you create with Drupal. The additional modules, mostly developed by members of the very active community, can be added as needed to expand the CMS’s functionality. Drupal supports relational database systems such as MySQL, MariaDB, Percona Server, and PostgreSQL.
If you’re planning to develop a community platform, weblog, or a journalistic website involving multiple editors, Drupal is an excellent choice.
How to set up and install the Drupal CMS
To use Drupal for creating your website, you must first establish the necessary software and hardware foundation for the installation and operation of the web software. The first step towards your own Drupal website is to find a server where you can install and host the CMS along with other required applications, such as the web server, database, or an FTP client.
Finally, you also need a suitable web address for your future web project. It is important to choose an address that is both meaningful and memorable. This can be quite challenging since many popular domain addresses are already taken. However, tools like the IONOS Domain Check can help you find your desired domain and check its availability.
What software is needed for using Drupal?
Regarding software requirements, they are similar to those of other popular content management systems:
- Scripting language: Drupal runs on any web server that supports PHP – for newer versions of the CMS, it is recommended to install current PHP 8 versions.
- Web server: The standard choice is the Apache web server, which is compatible with PHP; possible alternatives are NGINX or Microsoft IIS.
- Database: The Drupal team recommends MySQL, MariaDB, or Percona Server as the database management system.
- Operating system: Naturally, an operating system must be installed on your server, with Linux being the recommended choice.
If you want to use a proven software package that meets all the mentioned requirements, simply install the so-called LAMP stack.
Installing Drupal
If you want to manually install Drupal because you operate your own server or your provider does not offer prepackaged installation packages, you will first need the program files. The latest releases are always available for download on drupal.org. Use an FTP client like FileZilla to transfer the downloaded files to the root directory of your webspace. Then, access your Drupal project by entering your domain address in the browser of your choice, which will automatically redirect you to the installation page at /core/install.php. Follow the instructions of the Interactive Installer to set up Drupal.


How to create a website with Drupal step by step
To simplify your start, we’ve summarised the key steps regarding administration, page design, and content creation in Drupal below.
Step 1: Log in to the Drupal backend
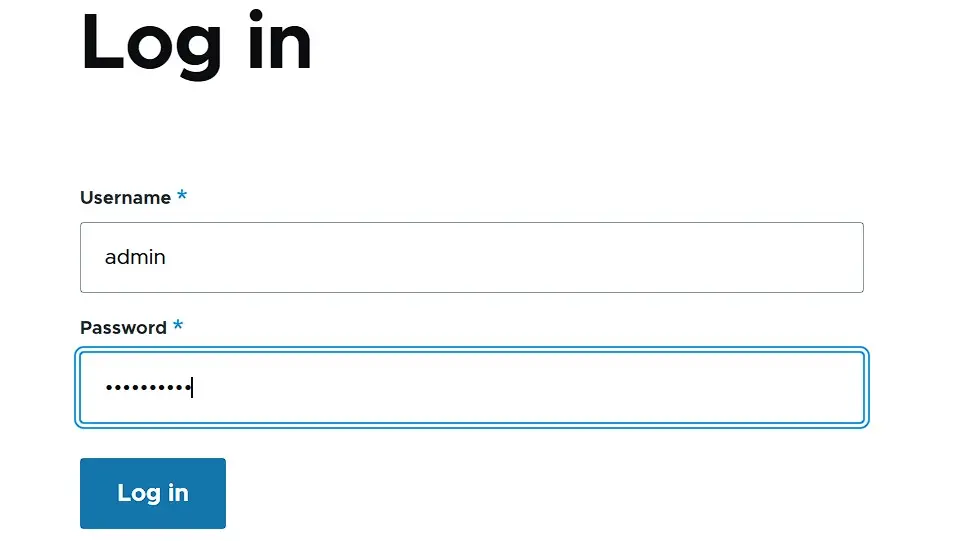
During the installation, you created an admin account for Drupal, which you will now need for logging in to the backend. Access the login window by using the web browser of your choice to visit the following address—simply replace the sample domain ‘example.org’ with the web address of your project:
https://example.org/user/loginIn the login screen, enter the admin username and the corresponding password, then click ‘Log in’:
Step 2: Change backend language
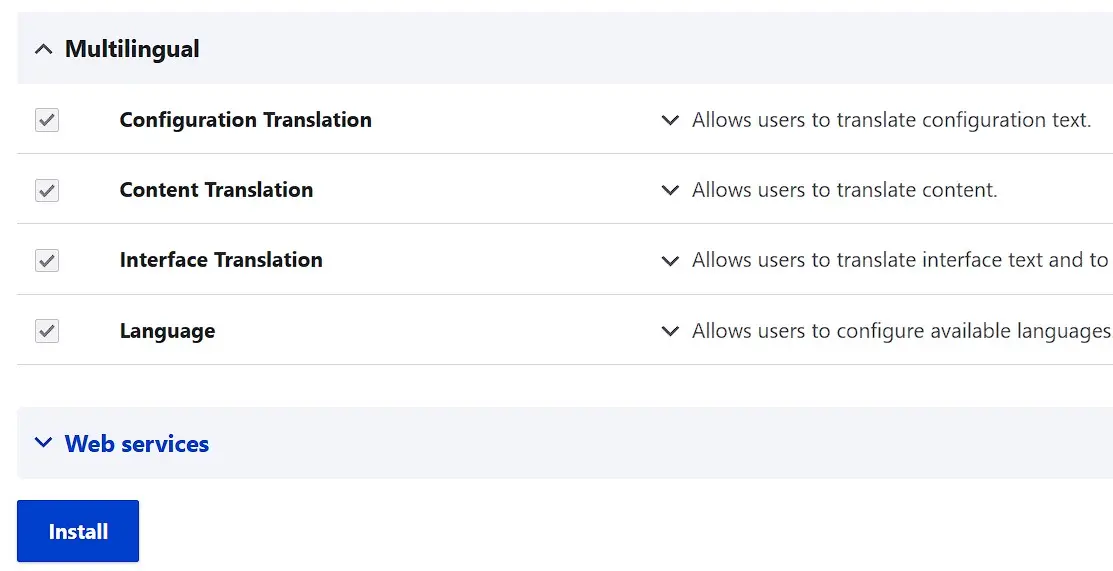
After installation, English is set as the default display language for the Drupal user interface. However, by installing language packs, you can select other languages if you want to. These packs are not part of the basic installation, so you must first activate the ‘Language’ module:
-
In the backend, open the settings menu ‘Extend’.
-
Scroll to the ‘Multilingual’ section and check the four available language and translation modules.
-
Scroll to the bottom of the page and press the ‘Install’ button.
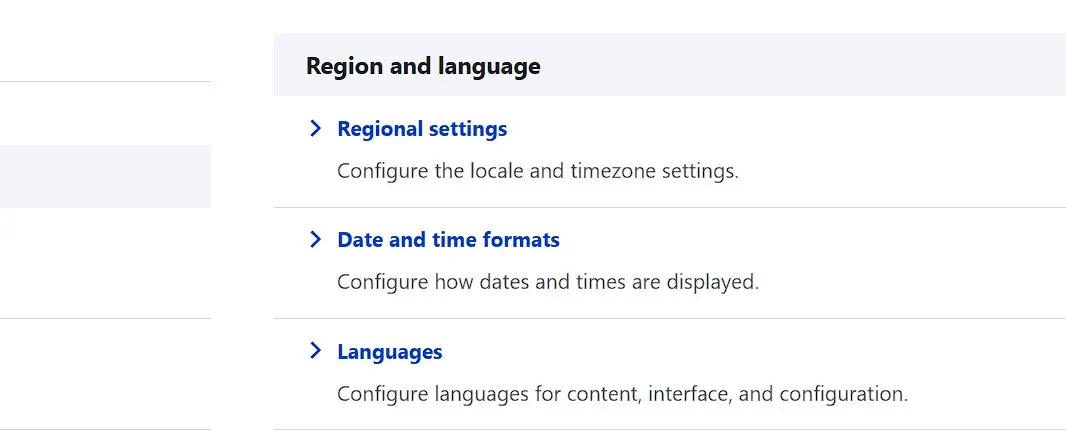
Switch to the ‘Configuration’ tab and in the ‘Region and language’ category, open the ‘Languages’ menu.
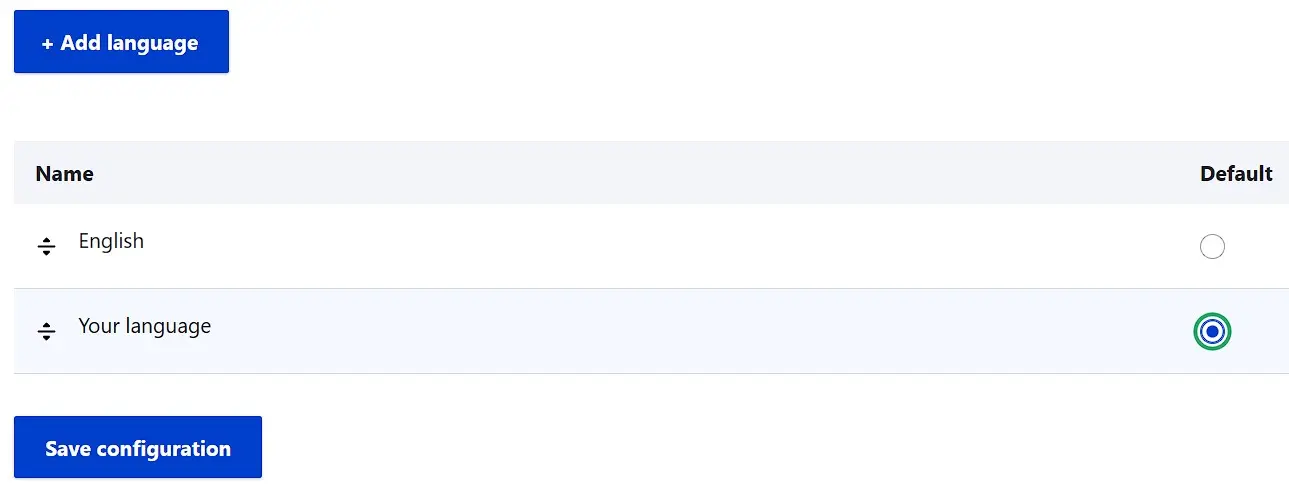
Click the ‘Add language’ button and select the desired display language for the backend before clicking ‘Add language’ again. In the final step, mark the desired language as the ‘Default’ language and save this choice by pressing the ‘Save configuration’ button.
Step 3: Managing users and roles
Before you start designing and creating your Drupal pages, you should consider the permissions for future users. The content management system allows you to create custom user groups for which you can define a complete set of permissions. You can then assign newly registered accounts to one or more of these groups, granting them the associated access and editing capabilities automatically. Three user groups are predefined in Drupal by default:
- Guest: Website visitors without registration in front or backend
- Authenticated user: Individuals who have created a regular user account
- Editor: Account for editors
- Administrator: Registered individuals with maximum rights
If you want to edit or delete these groups, or create additional ones, go to the user menu and switch to the ‘Roles’ tab:
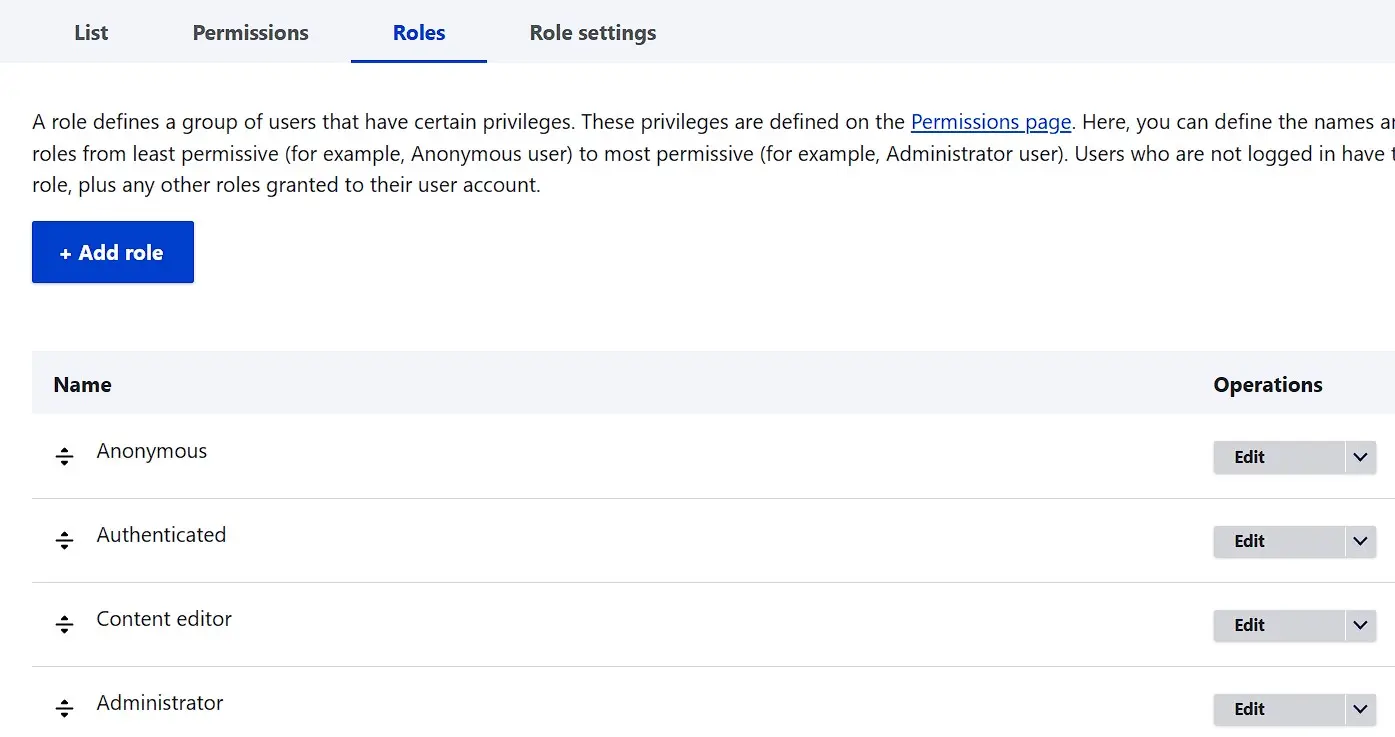
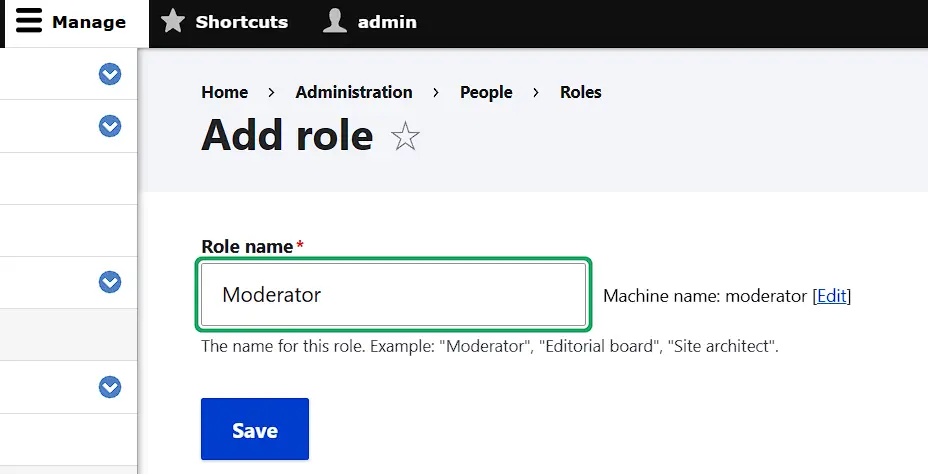
To add another group to the existing ones, click on the ‘Add role’ button. Then, enter a descriptive name and press ‘Save’:
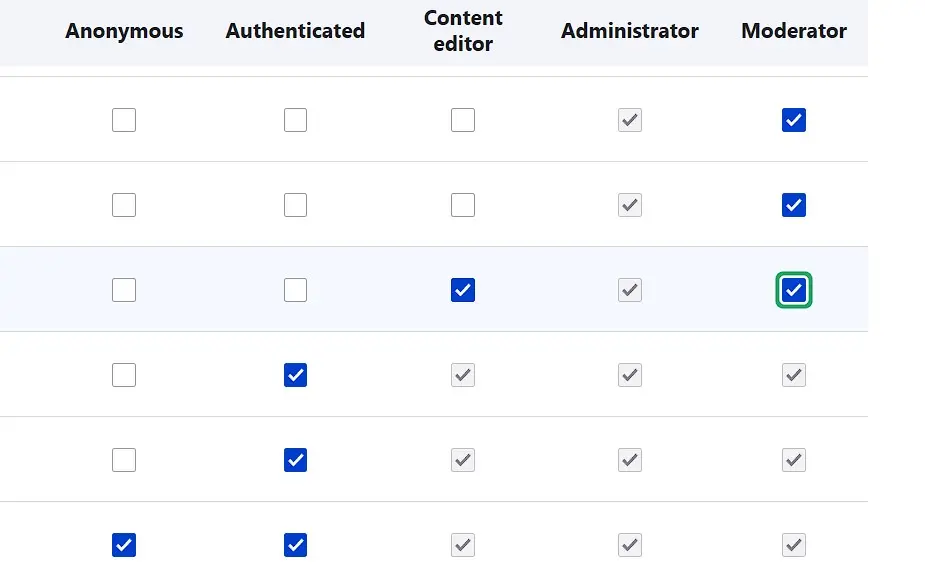
You then set the permissions for the new user group under the identical tab by ticking all the categories and actions the group should have, and finally, press ‘Save permissions’:
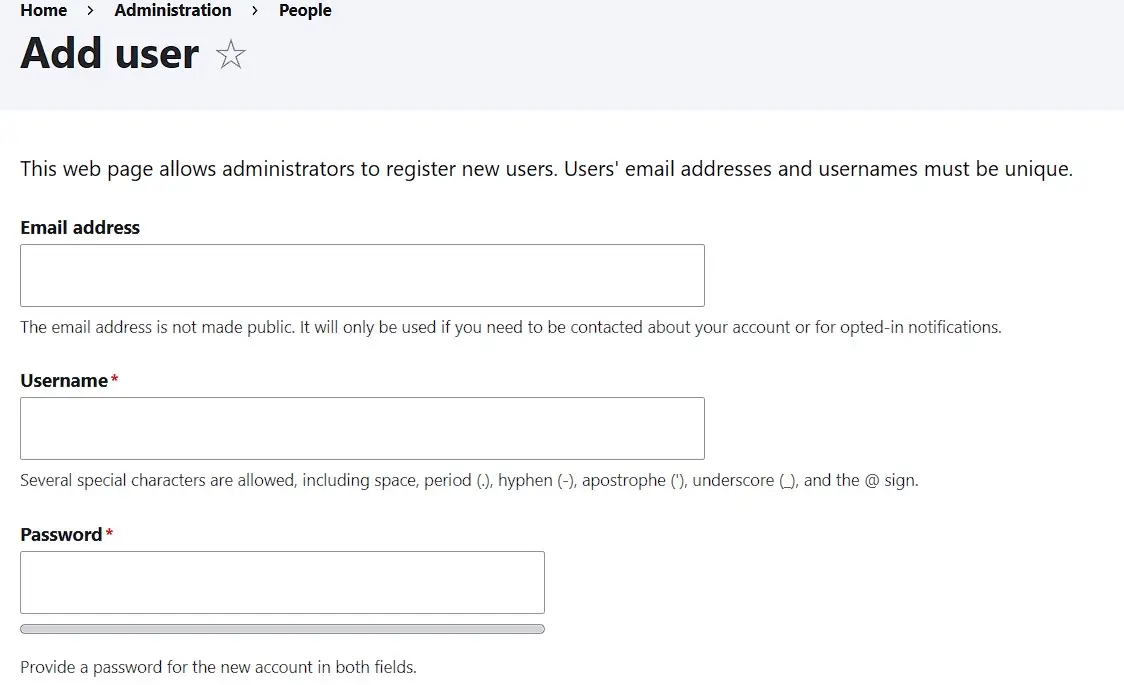
Creating a new user account is also done in the user menu. For this, open the start tab of the menu (‘List’) and click on ‘Add user’. Fill in the required information like email address, username, and password, then select the user group under ‘Roles’ to which you want to assign the new account. In the final step, add the new account via ‘Create new account’:
Step 4: Import theme and set as default theme
Creating a Drupal website is possible even for beginners with little IT experience, thanks to the simple structure of the content management system. Though the initial functionality is limited to the essentials, it doesn’t mean you can’t use the software for developing more complex projects. If the core components’ functions aren’t sufficient, you can easily add extra features through additional modules as needed.
When integrating additional modules and themes, always ensure that they are compatible with the version of Drupal you are using and originate from a trustworthy source, such as the official repository.
The principle of modular design also applies to the layout and design of your Drupal website: For this purpose, Drupal provides two pre-installed themes. The default theme Olivero and the administration theme Claro offer everything you need to start managing your project and creating your first Drupal pages. Alternatively, you can choose from hundreds of free Drupal themes in the Drupal Theme Repository, download, and add them to your Drupal installation. Unlike other CMS, Drupal does not offer an integrated installation manager for this purpose, so you need to manually move the theme to your web storage. The target directory is as follows:
/drupal/website-name/themesOnce you’ve moved the theme to the web storage, it can be installed via the backend of the content management system. To do this, open the ‘Appearance’ menu and scroll down to the section ‘Uninstalled Themes’:
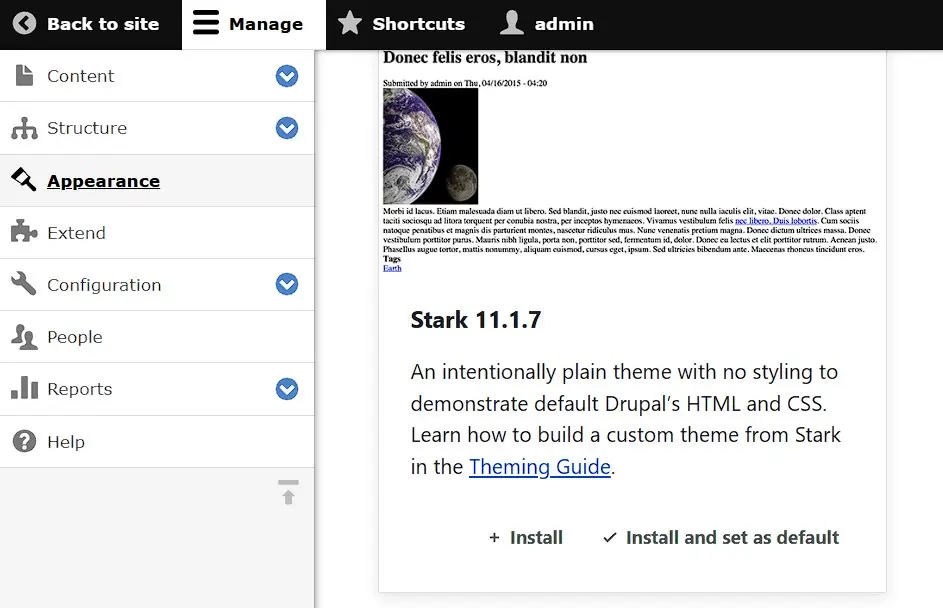
Click on ‘Install and set as default’ for the desired theme to install the template and choose it as the default for your Drupal pages. Finally, press ‘Save configuration’ to confirm the template change.
Step 5: Create Drupal pages
After you’ve completed the steps of backend configuration, user management, and layout selection, you now have the perfect foundation to start creating your Drupal website. The first step is, of course, creating new pages that can be filled with text, images, and videos. To create a new Drupal page, first go to the ‘Content’ menu and click on ‘Add content’:
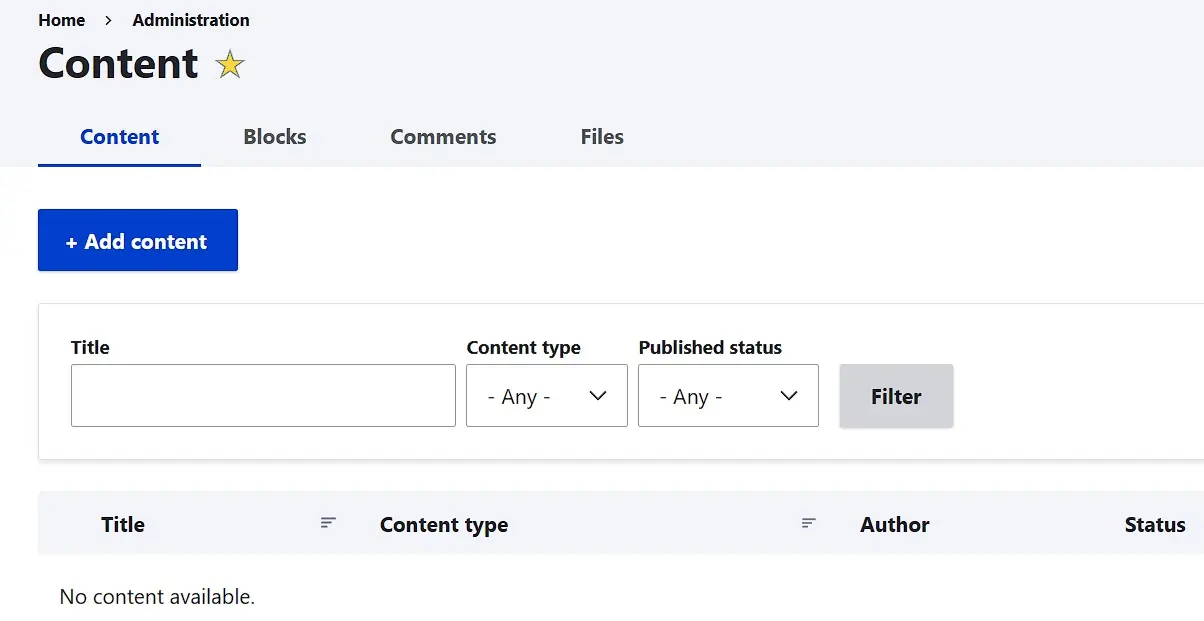
By default, Drupal provides two different types of pages:
- Select the type ‘Basic page’ for all web pages with static content, such as the ‘About Us’ page or the Privacy Policy.
- Use ‘Article’ for all pages with dynamic, time-sensitive content, such as blog posts, news pages, or press releases.
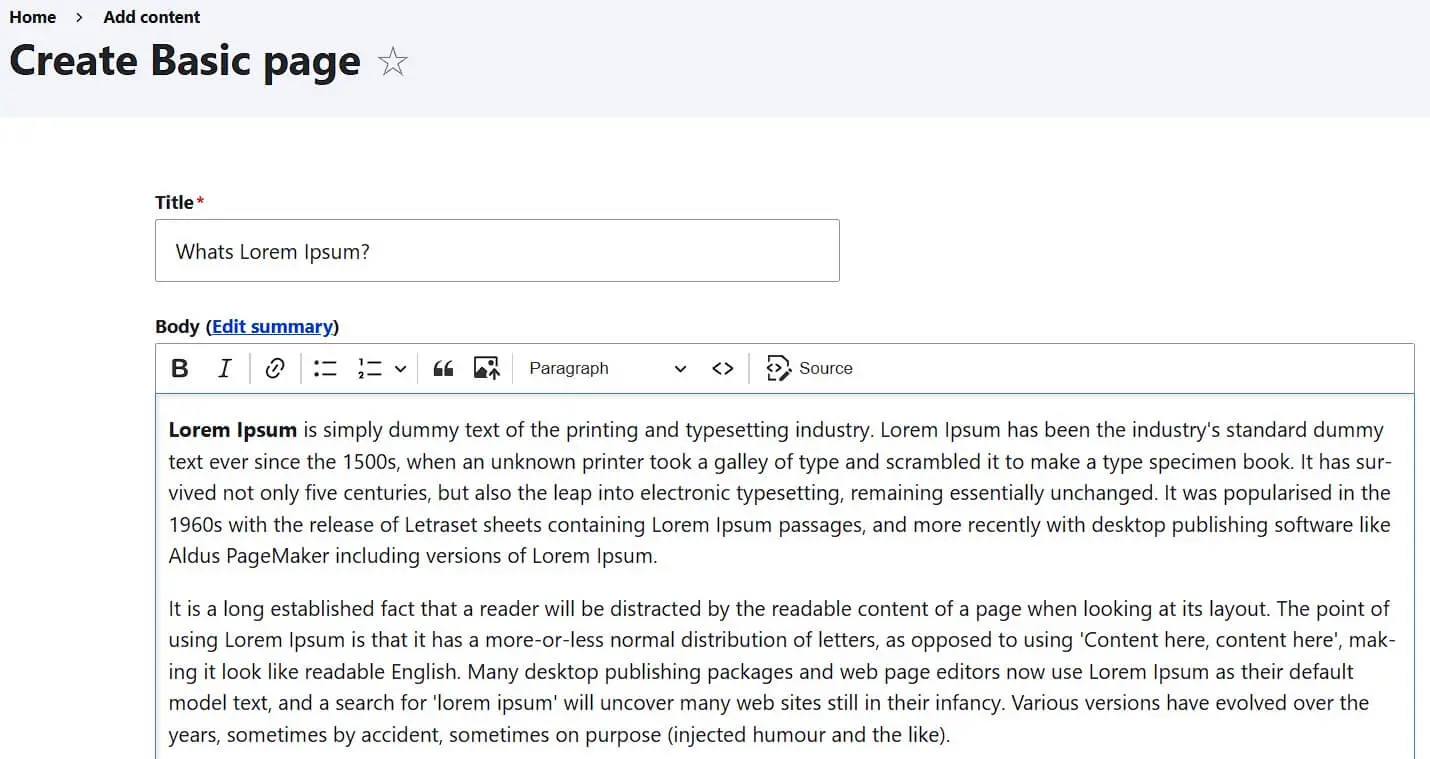
Simply click on the respective button to start creating a page of the desired type.
With both types of pages, you have the opportunity…
- to choose a page title,
- to insert text and
- to make initial menu and URL settings.
Exclusive features of the article pages include settings for comments, the application of tags, and the designation of an article image. Drupal requires only a page title as mandatory information for both basic pages and articles. With a click on ‘Save’, the new Drupal page can finally be created.
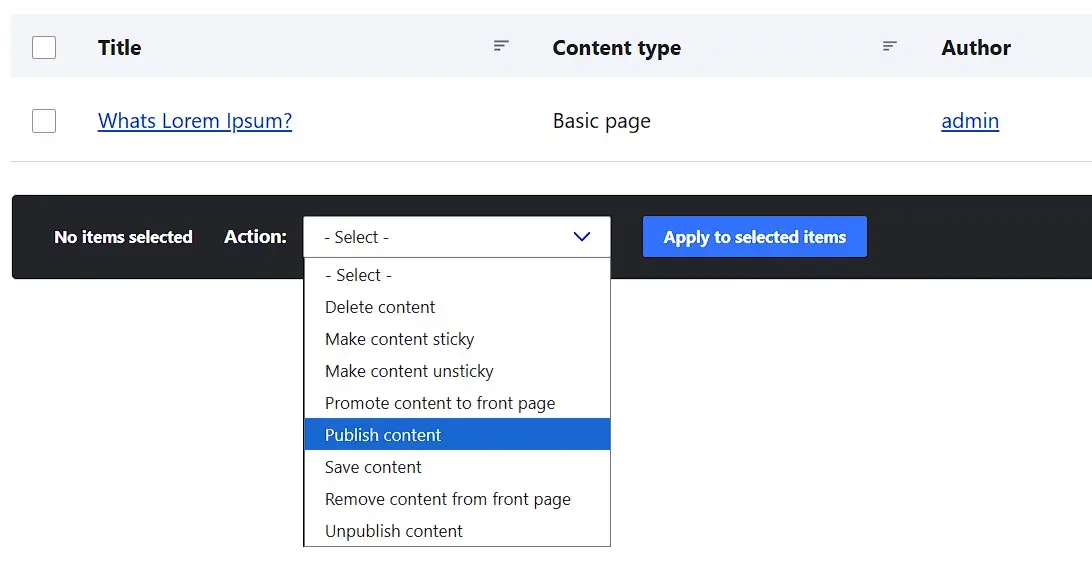
If you want to publish content on the website, check the appropriate page in the page listing in the ‘Content’ menu and select the desired publication option. Then, click on ‘Apply to selected items’:
Step 6: Insert images
If you want to add images to a text on your newly created Drupal website, open the edit editor for the respective page. Simply search for this page in the ‘Content’ menu and then click ‘Edit’. You will have the same settings options as when creating the page and thereby also access to the WYSIWYG Editor. With this, you can format the page text as in a regular text editor by using the toolbar to apply bold, italics, headings, or bullet points. Additionally, you can incorporate photos and images. To do this, first click on the image icon:
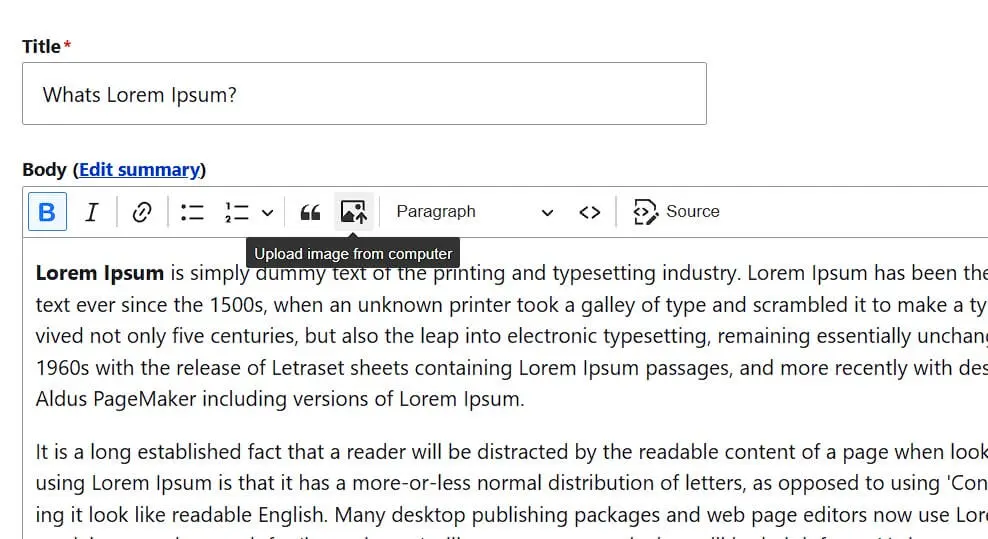
Specify the location of the image you want to embed on your Drupal page. Then, draft an alternative text that will be displayed to website visitors if they cannot see the image. A menu follows where you can set the alignment of the photo or graphic. Also, enable the table header so you can add a suitable caption under the image:
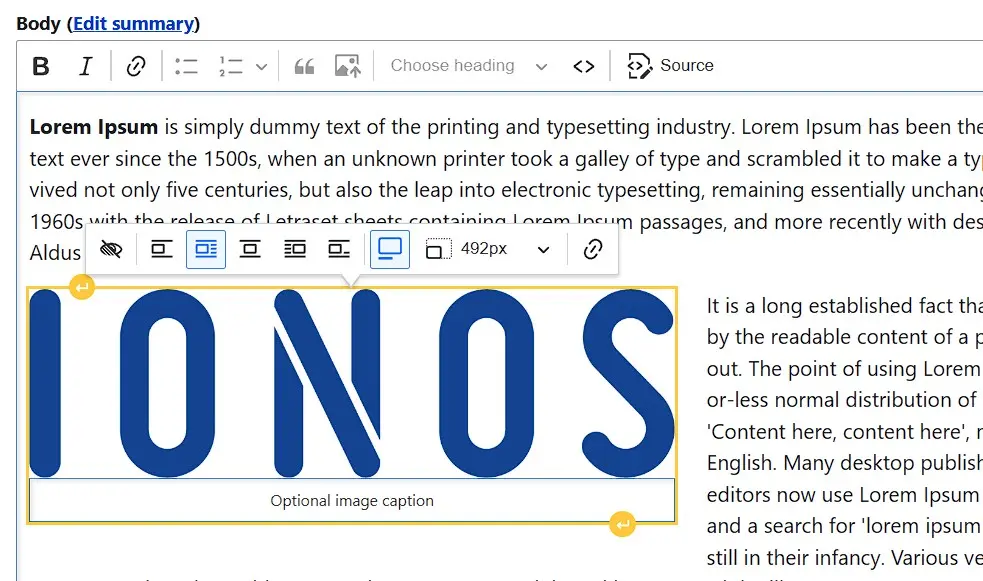
Step 7: Create links
The Drupal editor also allows you to create links by first clicking on the chain icon and entering the desired target URL. Then confirm the link by clicking the green tick or pressing the Enter key.
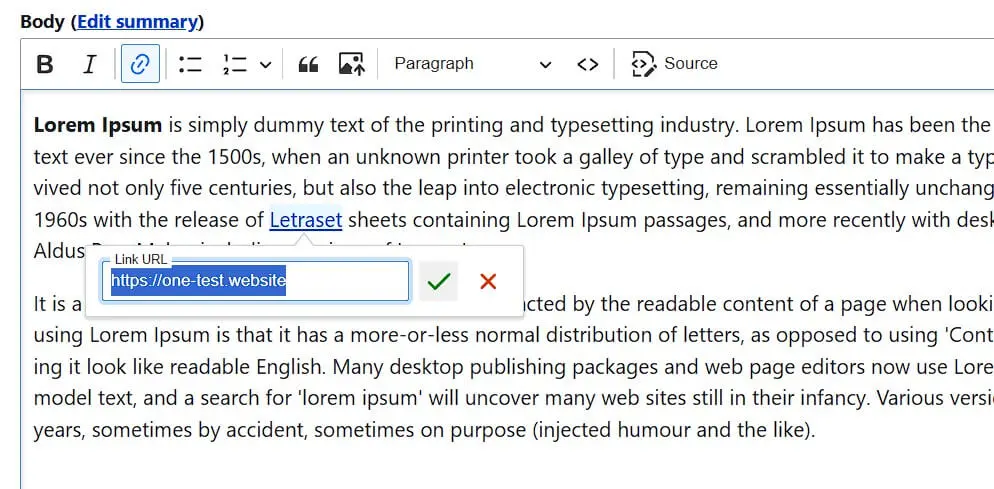
For internal linking, the standard method of linking is somewhat cumbersome, which is why there are various add-on modules that significantly simplify the procedure. We recommend the Linkit module, which is compatible with current Drupal versions. Download the appropriate Linkit file and transfer the module (as with theme installation) to your webspace. In this case, the target directory is:
/drupal/website-name/modulesOpen the ‘Extend’ menu and scroll to the ‘User interface’ section, where you can now select the Linkit module. Then scroll to the bottom of the page and click ‘Install’.

