How to encypt your emails with SSL/TLS
Sending emails without encrypting them means transmitting them over a vulnerable connection and in plain text. This allows unauthorised individuals to easily intercept and read these messages. With SSL/TLS, you can encrypt your emails and protect them from unauthorised access.
How to secure emails with encryption
The contents of emails, without encryption, are as secret as the contents of a postcard. If the card or email falls into the wrong hands, the entire text can be easily read. For this reason, powerful encryption methods have been developed to either create an encrypted email or encrypt the sending of an email. There are three categories when it comes to email encryption:
- Encrypt the transmission of emails
- Encrypt the content of emails
- Encrypt stored emails
How to send encrypted emails with SSL/TLS
The essential tool for securely sending email content is the universally applicable transmission protocol Transport Layer Security (TLS). It is better known by its former name Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). An email with SSL/TLS encryption is characterised by its content being indecipherable to outsiders during data exchange, as they do not possess the required key for decryption. It does not matter whether the email is accessed or sent via an email client like Outlook or through a web browser. SSL/TLS technology is used not only in email transmission but also, for example, in online banking or e-commerce.
When we talk about SSL/TLS today, in almost all cases we mean TLS. SSL is outdated and is no longer used for transmission encryption. In our article on TLS vs SSL, we explore the topic in more detail.
- Email protection on any device
- SSL/TLS email encryption
- Firewalls and spam filters offer first class virus protection
- Daily protection and backups
Encrypted emails with S/MIME or PGP
If you want to encrypt the actual content of emails, you have various techniques available – like the standard method S/MIME or the well-established PGP, both of which use asymmetric encryption. While traditional methods access the same key for coding and decoding, asymmetric encryption involves two keys – a private key, known only to the sender, and a public key, freely accessible to all recipients.
Encrypt saved emails using software
The encryption of electronic messages is crucial even when they remain stored in your inbox or archive after being read. Such encryption ensures you are prepared in case criminals gain access to your account and thereby access to all existing emails. You can ensure additional protection through two-factor authentication (especially when using web email clients) or through encrypting your data or the relevant folders and files (when using desktop email clients or apps).
How to put email encryption into practice
The most important building blocks for email encryption and secure message transmission have been briefly explained in the preceding sections. In the following sections, you will learn more about how to implement the individual security measures.
Encrypt email transmission in web clients
Reputable email providers have long offered their web services over the secure HTTPS protocol as standard. You can recognise this by the URL, which begins with ‘https’ instead of ‘http’. Additionally, in your browser’s address bar – typically indicated by a lock symbol – you can check if the webmail client has an SSL/TLS certificate.
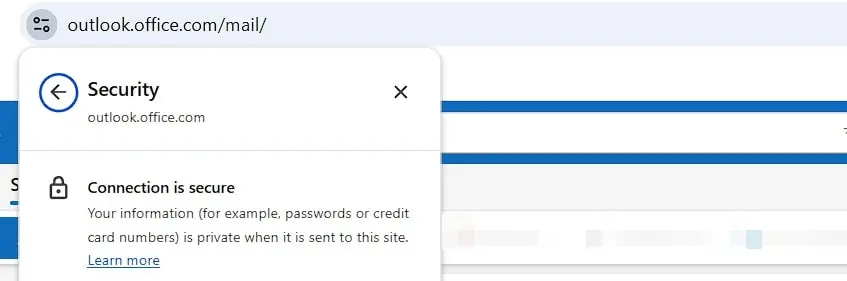
Encrypting email transmission in desktop clients
Even in the mail client on your PC or in a corresponding app on your smartphone or tablet, you can encrypt the connections to the email server using SSL/TLS. The crucial element that needs to be defined for this is the port, used for sending or receiving. You can find the relevant settings in the account settings of the respective mail program. There is often a general option to activate mail SSL/TLS encryption. Once this is enabled, the program usually configures the appropriate ports automatically. Otherwise, you can do this manually, where you will need to enter different numbers depending on the type of incoming server (POP3 or IMAP) and for the outgoing server:
- Incoming mail server (IMAP): 993
- Incoming mail server (POP3): 995
- Outgoing mail server (SMTP): 465
Select ‘SSL’ as the connection type. (Technically ‘TLS’ despite the ‘SSL’ label.)
If the StartTLS function is activated in the options, SMTP Port 587 (less commonly Port 25) is required for establishing encrypted connections using this technique.
Encrypt email content (example: Mailvelope)
If you want to send and receive encrypted emails as well as use a secure SSL/TLS connection, you have numerous programs at your disposal with which you can access the S/MIME and PGP encryption methods previously mentioned. If you send and receive your email using a web client, the easiest way is to use a browser extension such as Mailvelope, which will be used as an example in this article.
Mailvelope is available for Firefox, Edge, and Google Chrome, allowing you to use PGP email encryption in various webmail services. The first step is to install the extension through the plugin or extension centre (direct links can be found on the Mailvelope homepage).
When you launch the extension after installation, a popup window will appear. Click on ‘Let’s start!’ to start the configuration. You will then be redirected to the key management, which at this point logically doesn’t contain a key pair for the planned email encryption yet. To generate this, click on ‘Generate Key’ and then enter the requested information:
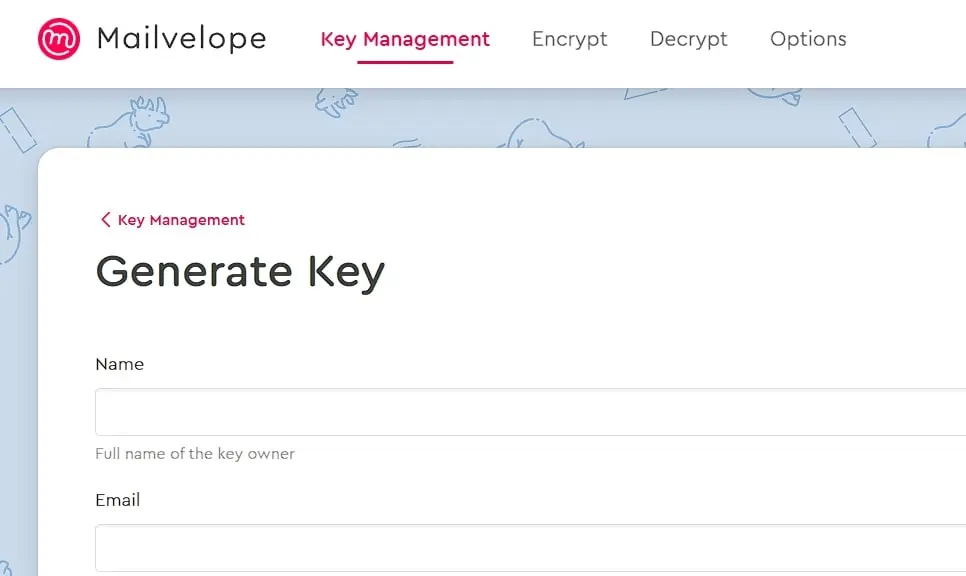
Select the option ‘Upload Public Key to Mailvelope Key Server’, allowing your contacts to obtain it from there to send you encrypted emails as well. Once the PGP key pair is generated, you will receive a success notification and an initial encrypted email sent by Mailvelope to the specified email address. Open the message, click the icon in the middle (‘Show Message’), and then enter the password for the previously created key:
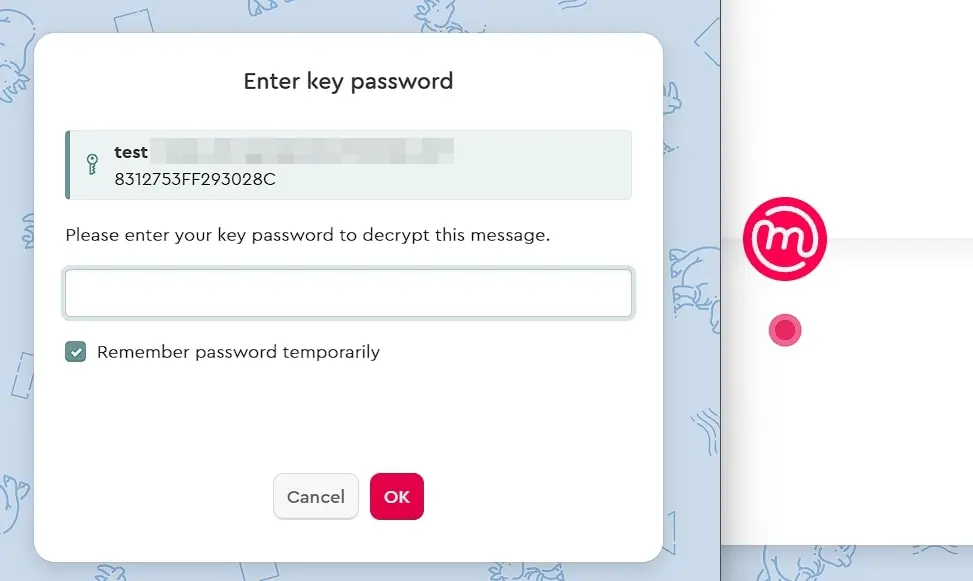
The message will be decrypted, and a link will become visible. Click it to activate your email address and be able to encrypt emails in the future. For encryption, you will now find a specific Mailvelope button in the message editor of the respective web client, which you must always use when you want to encrypt the content of emails:
- Email protection on any device
- SSL/TLS email encryption
- Firewalls and spam filters offer first class virus protection
- Daily protection and backups
Email encryption with IONOS Mail
IONOS email servers have permanently disabled outdated TLS versions and SSL. If you’re using IONOS Webmail, there’s no need for concern—encryption is automatically and consistently enforced.
When using IONOS Mail in an email program on your PC or cell phone (e.g., Outlook, Thunderbird, Apple Mail), make sure that SSL/TLS encryption is enabled.
To enable SSL/TLS in your mail client, proceed as follows:
- Open the mailbox settings.
- Enable SSL/TLS encryption for the mailbox.
- Set the correct ports for incoming and outgoing mail servers:
- Incoming via POP3 (SSL/TLS): 995
- Incoming via IMAP (SSL/TLS): 993
- Outgoing via SMTP (SSL/TLS): 465
How to enable encryption for IONOS Mail on Android, iOS, and more can be found in the article on switching to SSL/TLS encryption in the IONOS Help Centre.

